-
Water diversion
Diverting water away from its natural channel for commercial or private use. -

Sediment and urbanisation
How does urbanisation increase sediments in waterways? -

Lake Ōmāpere and the Utakura River
Tuna harvested from Lake Ōmāpere and Utakura River catchment have long comprised an important fishery for tangata whenua. -
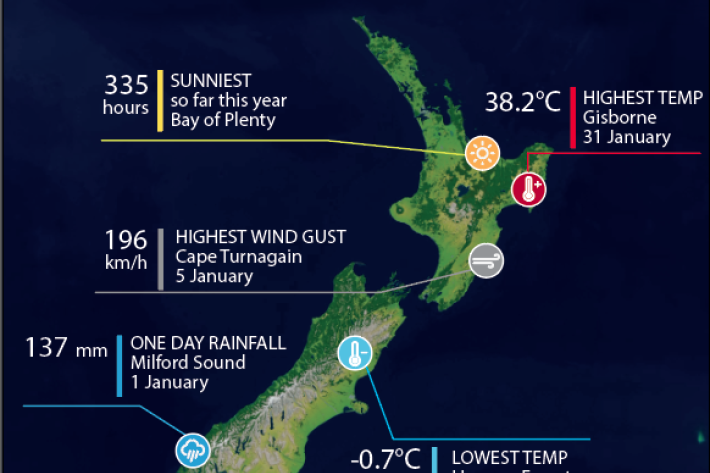
Climate data and activities
We provide an overview of New Zealand climate data for use in school projects. -

Electronic Weather Station - NIWA EWS
These gather top-quality data and are used throughout New Zealand in the National Climate Network. -
Identification guides
Useful information and resources on New Zealand's marine flora and invertebrate fauna. -

Giant kōkopu
The largest member of the Galaxiidae family. -

Modified habitat
A habitat is an environment or place where animals normally live. -

Tuna - identification
There are several ways to tell the three New Zealand eel species apart. -

Climate summaries
Education ResourceIn this climate education resource, you can download this climate summary in a range of formats.
