-

Tuna - glass eels
Glass eels (about 5.5 to 7.0 cm) arrive in fresh water during spring, especially during September and October, although they may be present from July to December. -

Monthly
Publication seriesMonthly climate summaries from December 2001 to the present. -

Mean daily maximum temperatures (°C)
These datasets are available in a range of formats. -
El Niño maps and charts
View a collection of maps showing the impact of past El Niño and La Niña events. -

Map E South
Education ResourceThe climate of this zone is greatly dependent on the lie of the massive Southern Alps to the west. -
Northland
Northland, with its northern location, low elevation and close proximity to the sea is characterised by a mild, humid, and rather windy climate. -
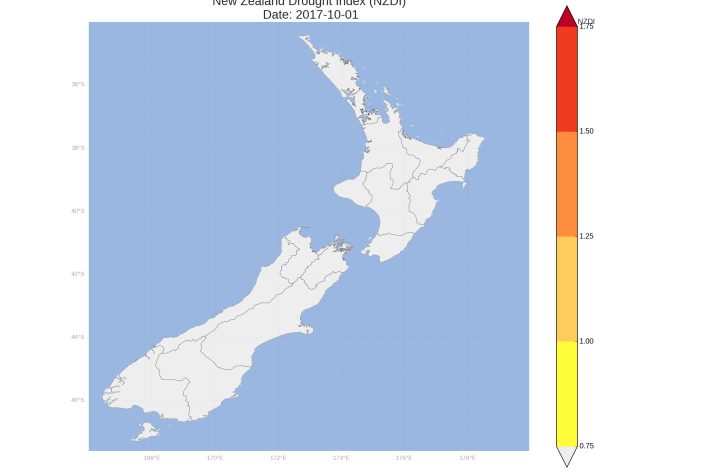
New Zealand Drought Monitor
ServiceThe New Zealand Drought Monitor is a system for keeping track of drought conditions across New Zealand based on a standardised climate index. -

NIWA staff profile: Nava Fedaeff
Feature story06 June 2017At the age of seven, NIWA’s youngest climate scientist, Nava Fedaeff, swapped sub-arctic Siberia for balmy Auckland – and her first job was to learn to swim. -

Daily climate maps
These climate maps are updated daily and are based on data from our National Climate Database. -
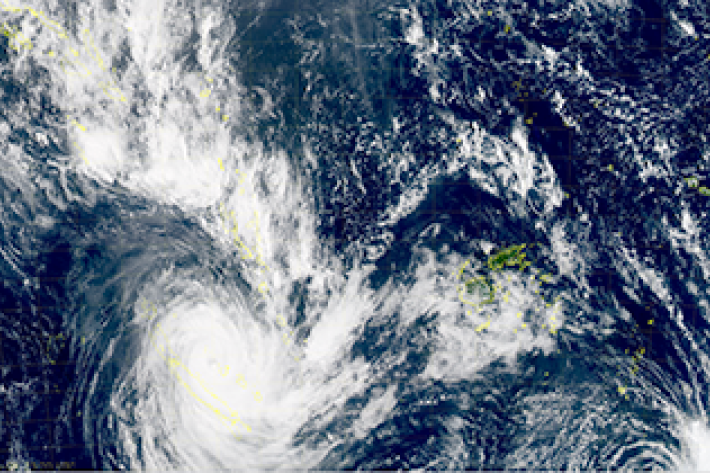

Tropical Cyclone Cook churning across Pacific
Media release10 April 2017NIWA meteorologist Seth Carrier outlines the likely path of Cyclone Cook, which is gaining strength in the Pacific.


