-

Chemical contamination and wastewater
What are the potential sources of chemical contaminants in wastewaters? -

Further reading
References, further reading, and links to useful websites. -
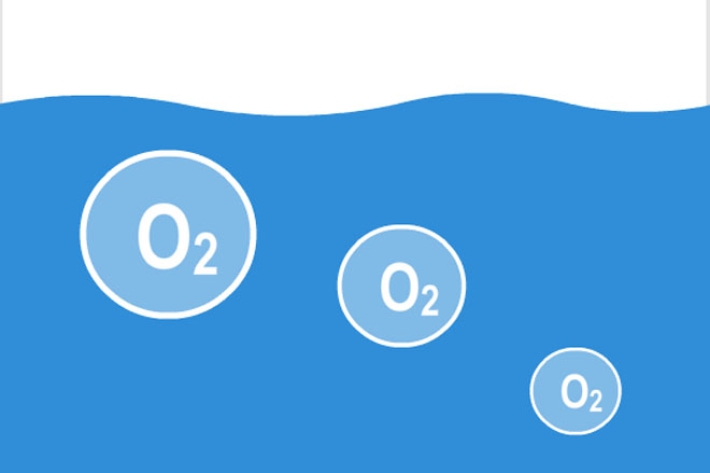
Dissolved oxygen
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is a relative measure of the amount of oxygen (O2) dissolved in water. -

Impacts of wood processing
Impacts of timber processing activities on water quality and mahinga kai. -

Riparian vegetation and agriculture
How may agricultural activities impact riparian vegetation around a waterway? -
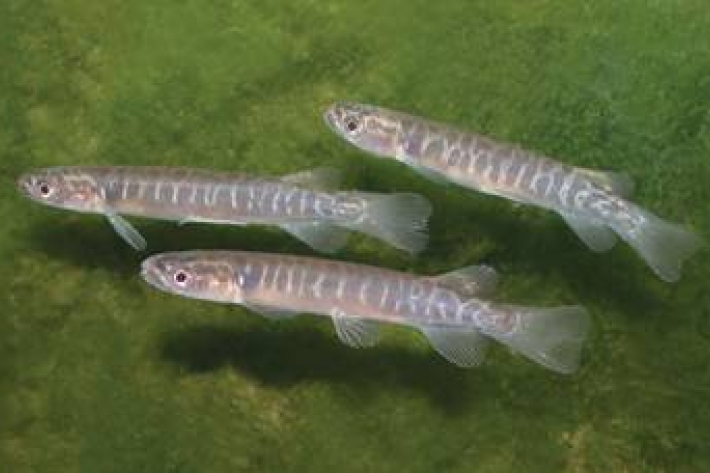

Mahinga kai - what species interests you?
In Kaitiaki Tools the term mahinga kai generally refers to indigenous freshwater species that have traditionally been used as food, tools, or other resources. -

Chemical contamination and aquaculture
What are the potential sources of chemical contamination from aquaculture activities? -

Chemical contamination and mining
What are the potential sources of chemical contamination from mining activities? -
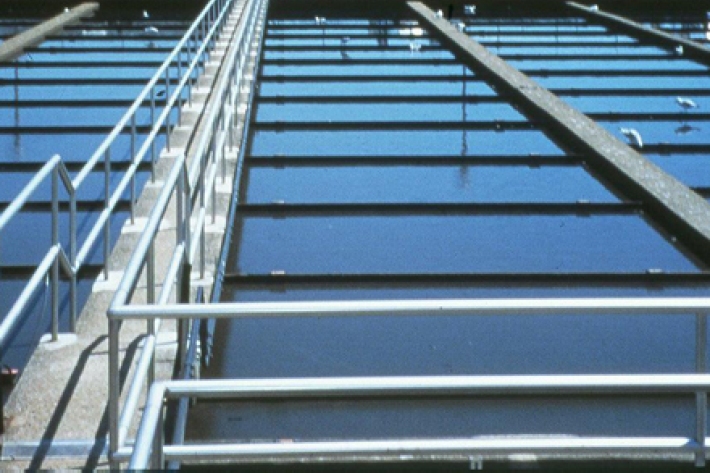

Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment is the separation and extraction of solid waste from liquid waste, and the removal of nutrients and pathogens. -

LakeSPI: Keeping tabs on lake health
Software Tool/ResourceThe condition of many NZ lakes is under threat from land-use changes and the invasion of alien aquatic plants. -
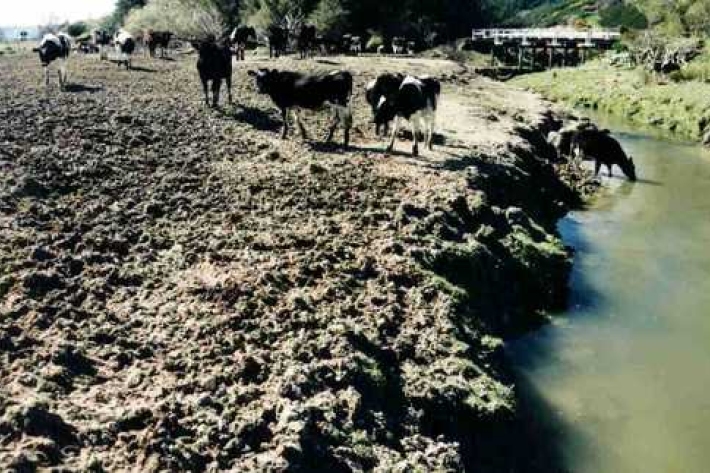

Loss of riparian vegetation
Plants and trees along the water margins and banks are called riparian vegetation.


