-

UVI smartphone apps
Several apps that provide forecasts of the UV index (UVI) are available for smartphones. -

'Eleven-station' series temperature data
Research ProjectTemperature trends from 1930s to present day -

West Coast
West Coast is New Zealand’s wettest region, and this may be attributed to its exposure to the predominant westerly airflow over the country, combined with the orographic effect of the Southern Alps. -
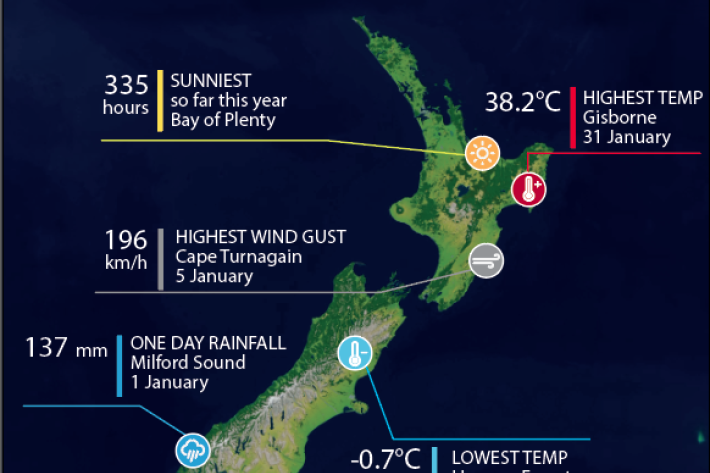
Climate data and activities
We provide an overview of New Zealand climate data for use in school projects. -

How do we determine past climate?
Information about past climate is obtained from piecing evidence together from various sources. -
Otago
The climate of Otago is perhaps the most diverse of any region in New Zealand. -

PARTneR (Pacific Risk Tool for Resilience)
Research ProjectUnderstanding how hazards impact people and the environment provides the foundation for informed decision making for a resilient Pacific. -

Mean 10cm earth temperature (°C)
These datasets are available in a range of formats. -

Southwest Pacific Tropical Cyclone Outlook
Publication seriesA summary of up-coming tropical cyclone seasons, issued 6-monthly.