-
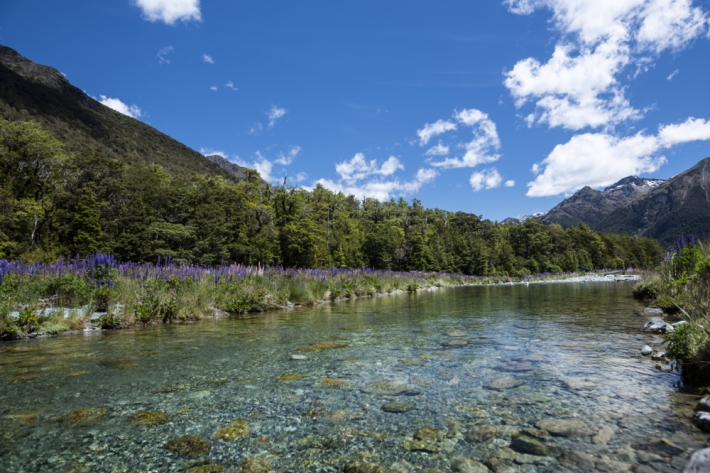

Dramatic changes in New Zealand river flows, research finds
Media release23 March 2023River flows in New Zealand have changed dramatically over the past 50 to 90 years as the climate has varied, a new study has found. -
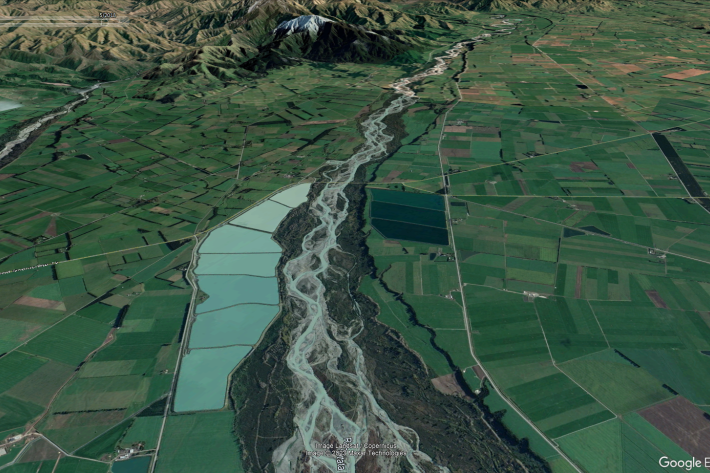

New Zealand streamflow depletion model: A tool for sustainable water resource management
As the concerns over water resources and the environment increase, the importance of combined water management, which acknowledges the integrated nature of groundwater and surface water, and manages them as a single resource, is critical to sustain both human society and aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. -

Half of NZ’s rivers blocked for migratory fish
Media release25 January 2023Nearly half of New Zealand’s river network is partially or fully inaccessible to migratory fish, a new study shows. -
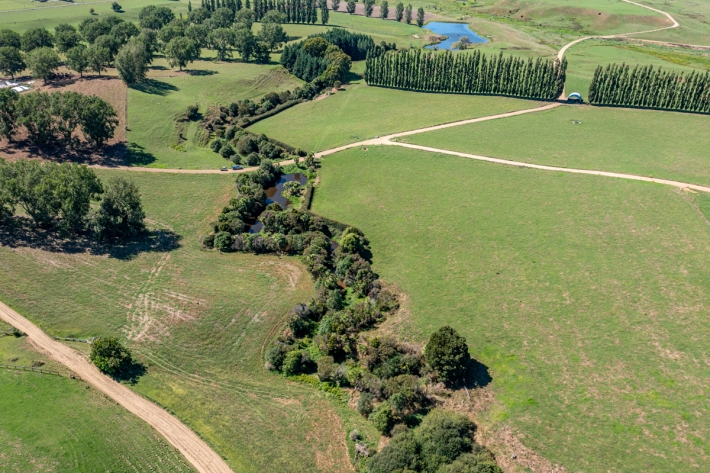

Riparian Buffer Design Guide
This guide discusses design principles and provides high-level information about the likely performance of riparian buffers. -
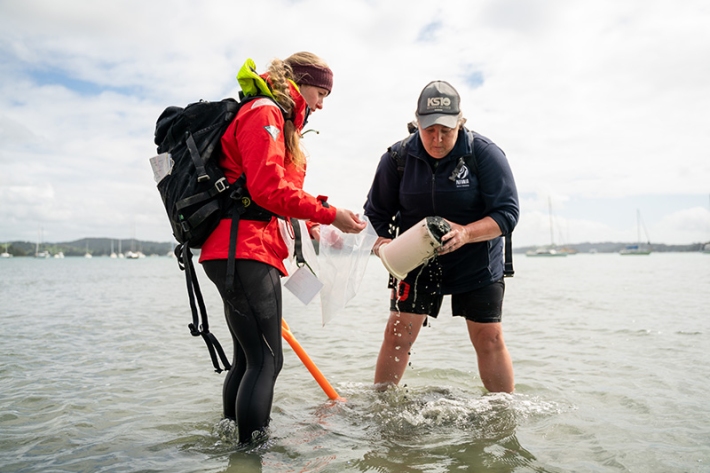

Ki uta ki tai: NIWA’s role in mountains-to-sea estuarine management
Media release09 June 2022Estuaries are coastal waterbodies where freshwater mixes with seawater. Many estuaries in Aotearoa New Zealand have been impacted by pollutants and contaminants entering via freshwater. -
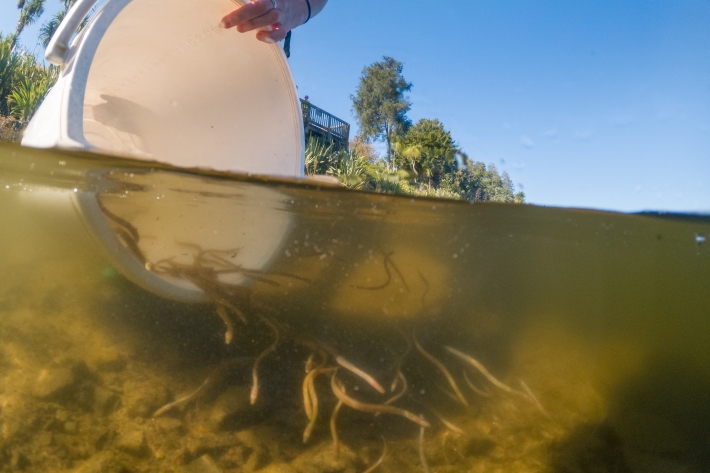

Removing barriers to ensure freshwater fish can complete their life cycle
Media release19 May 2022New Zealand has just over 50 native freshwater fish species. Of these, 85 % are endemic and 75 % are deemed to be at risk of decline or are threatened. -
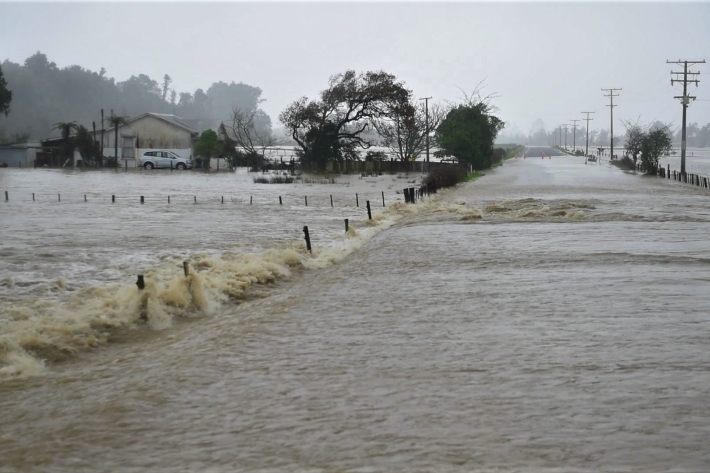

Public asked to help build national flood photo database
Media release15 February 2022NIWA is asking people in flood-affected areas to contribute photos to a national database to support understanding of flood hazard and flood risk. -
Waikato Dynamic Models Project Proposal
Protection of the Awa Models enable us to predict how different uses of the land and water will impact river and stream health. -

Report: Trends analysis for selected indicators of Waikato River health and wellbeing 2010-2019
ServiceReport: Trends analysis for selected indicators of Waikato River health and wellbeing 2010-2019 -
The largest flood flow ever measured
Media release29 July 2021Flood flows on the Buller River this month were the largest of any river in Aotearoa New Zealand in almost 100 years, NIWA measurements show. -
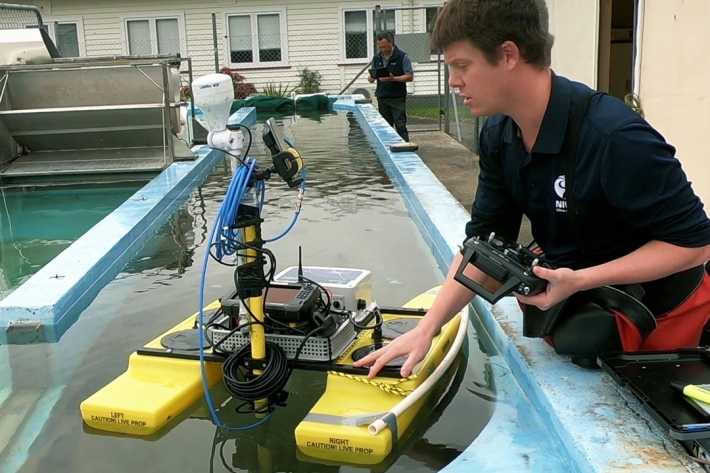

New weapon in fight against invasive aquatic weeds
Media release20 July 2021A combination of artificial intelligence and scientific ingenuity looks set to be the next step forward in protecting Aotearoa New Zealand’s lakes and rivers from invasive aquatic weeds. -

Trustpower's Waipori power scheme
or over 100 years Trustpower's Waipori power scheme has supplied Dunedin with hydroelectric power.

