-

Hotspot Watch Updates
This weekly update helps assess likelihood of extremely dry weather preceding a drought. -
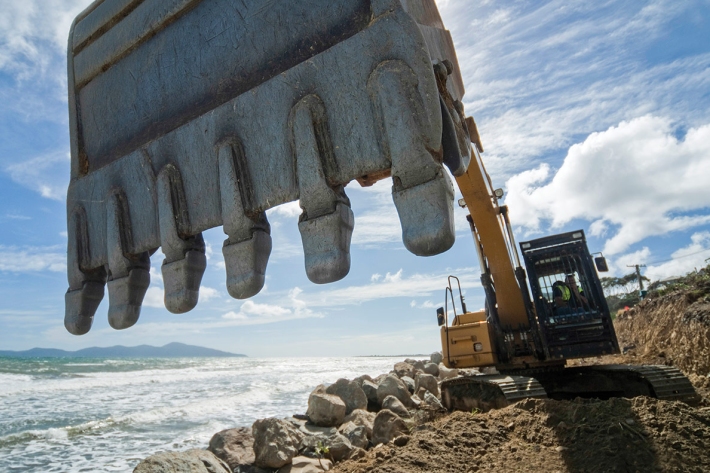

Shifting Sands – the end of a Kiwi dream
Feature story06 June 2017The Kiwi dream of owning a beachfront property with panoramic views of the ocean is under threat—and not just for financial reasons. -
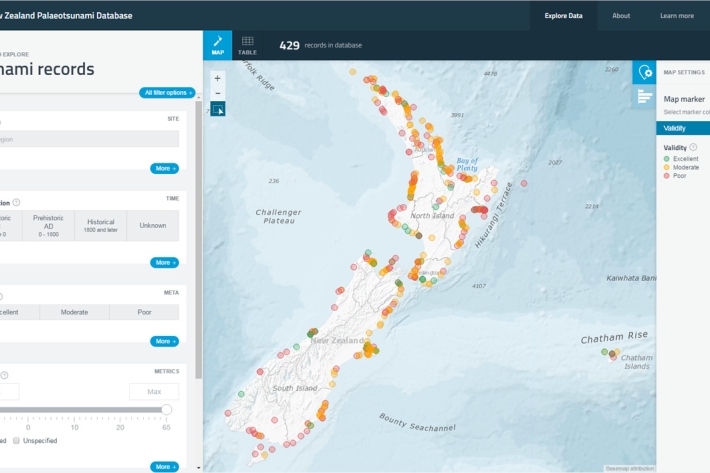
New Zealand Palaeotsunami Database
Software Tool/ResourceThe New Zealand Palaeotsunami Database (Database) brings together all known information about tsunamis that occurred prior to written records. -
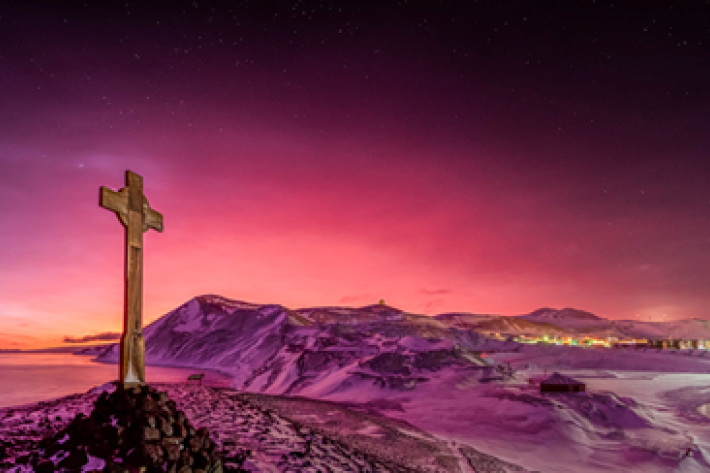

Tonga volcano “afterglow” causes dazzling skies in Antarctica
Media release06 June 2017Antarctica is experiencing stunning skyscapes like those recently seen in New Zealand, thanks to the afterglow effect from the Tongan volcano. -
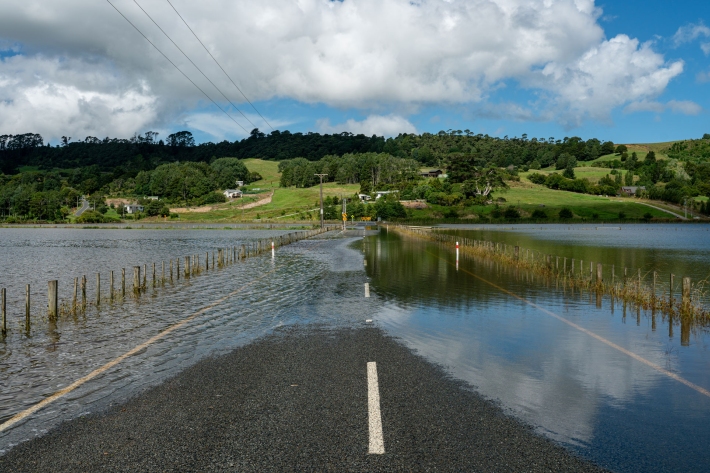

Flooding - how does it happen?
Education ResourceUnderstanding what happens above and below ground during a flooding event, and how it is different from normal rainfall conditions -
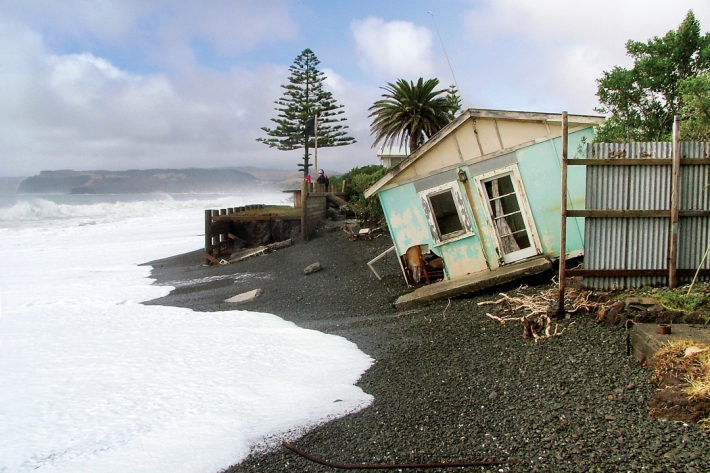

Sea-level rise
Education ResourceOne of the major consequences of climate change is rising global sea levels. -
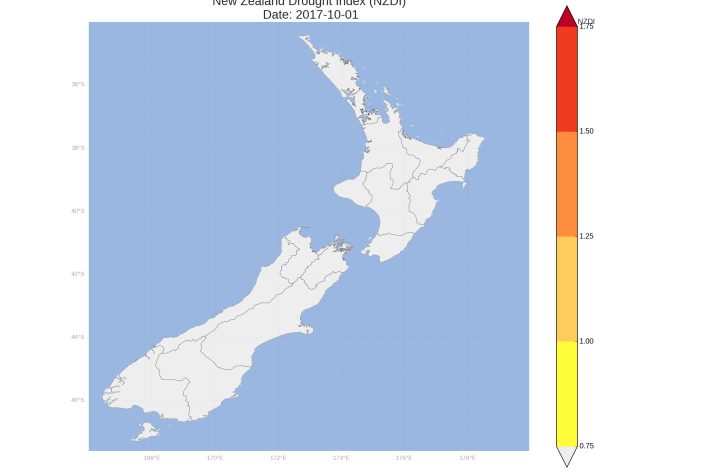
New Zealand Drought Monitor
ServiceThe New Zealand Drought Monitor is a system for keeping track of drought conditions across New Zealand based on a standardised climate index. -

Wave action
Feature story06 June 2017New Zealand’s coast is sculpted by ocean waves. Some wave conditions bring joy to surfers and beachgoers, but, at other times, waves can cause major hazards at sea or along the shore. -

Kiribati plans for climate change
-

Marine geological hazards
Education ResourceNew Zealand faces a variety of hazards associated with undersea geological activity. -

Droughts
Generally speaking, a drought is defined as a rainfall deficit which restricts or prevents a human activity – for example, farming or power generation.

