Note: Kaitiaki Tools were developed to assist people involved in the resource consent process and focusses on the potential impact of land-use change or point source discharges on freshwater mahinga kai. This project was completed in 2011. Some information may be outdated.
Different land uses and point source discharges can cause a variety of environmental impacts on water quality and mahinga kai.
-
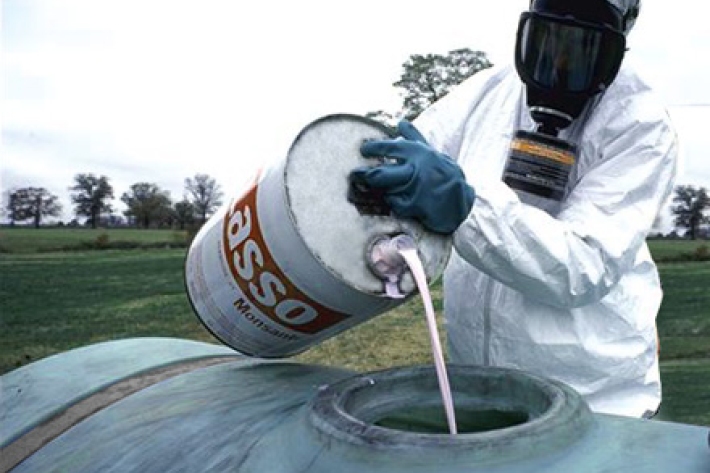

Chemical contamination
Chemical contaminants are chemicals toxic to plants and animals in waterways. -

Mitigation and best practice options
Some simple steps to minimise the effects of wastewater on water quality and mahinga kai. -
Dissolved oxygen
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is a relative measure of the amount of oxygen (O2) dissolved in water. -

Infectious substances
Waterways can easily become contaminated by pathogens when effluent is discharged nearby. -
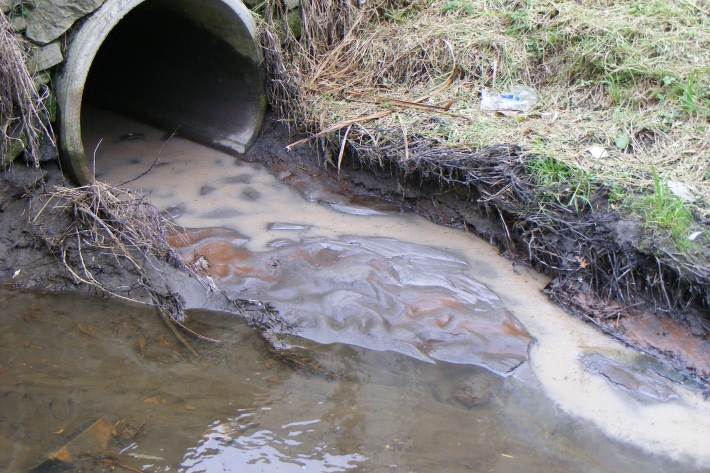

Instream barriers and altered water flow
Instream barriers and diversions alter the natural flow of rivers, streams, and lakes. -

Modified habitat
A habitat is an environment or place where animals normally live. -
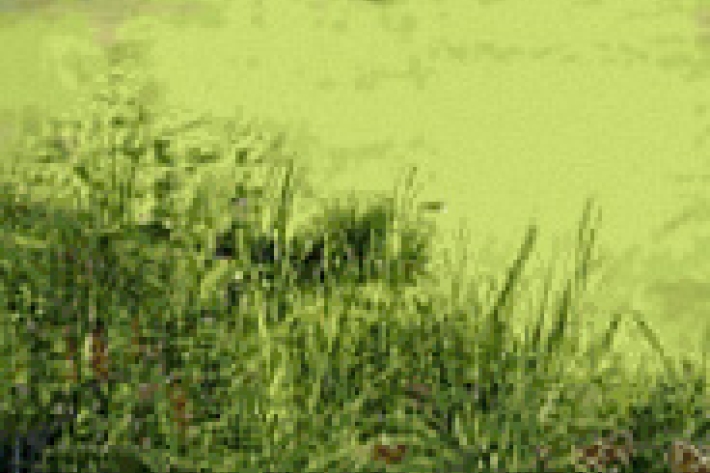

Nutrient overloading
Nutrients in waterways are essential for the growth of algae and aquatic plants but too much can destroy an ecosystem. -
Sediment
When soils erode, sediments are washed into waterways. -

Temperature changes
Temperature affects the number and type of animals and plants that live in a waterway. -

Water clarity
Water clarity or turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness in a fluid caused by individual small particles (suspended solids). -
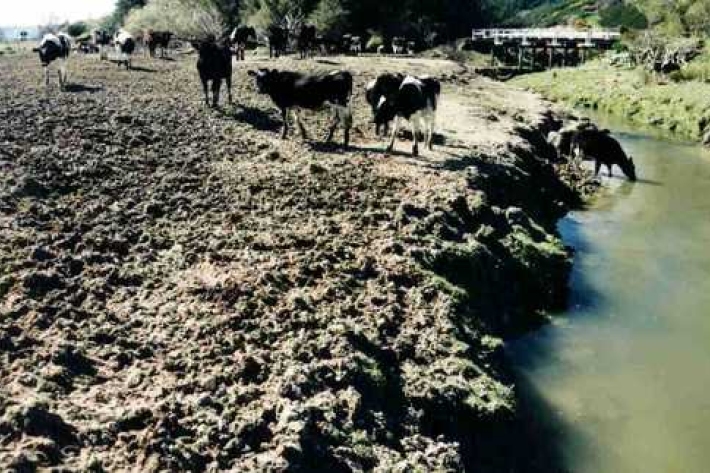

Loss of riparian vegetation
Plants and trees along the water margins and banks are called riparian vegetation.
