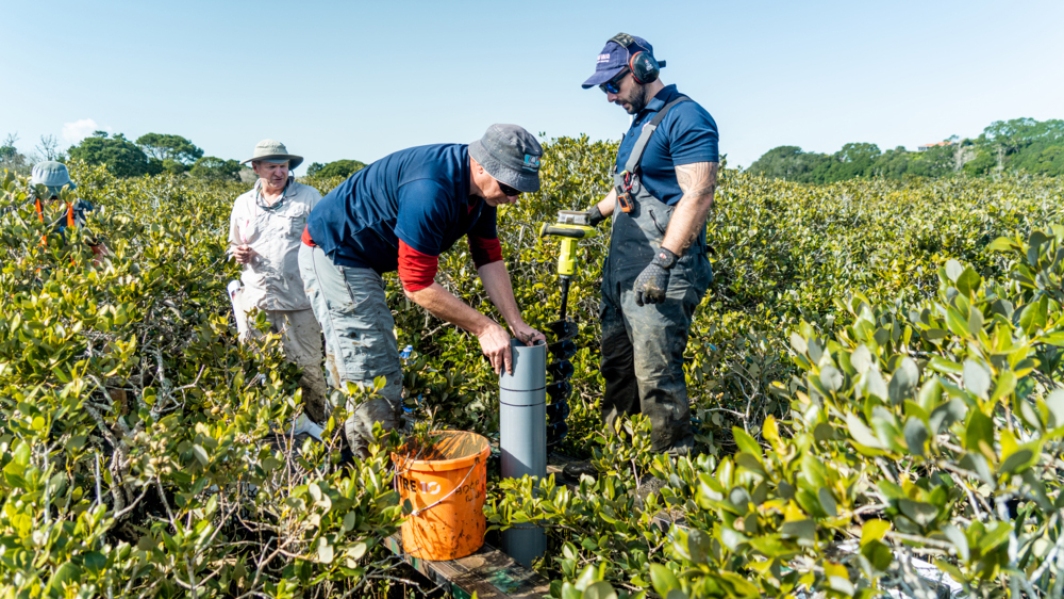
-

Category E - Tidal lagoons or barrier enclosed lagoons
Shallow, circular to slightly elongated basins with simple shorelines and extensive intertidal area. -

Category D - Coastal embayments
Shallow, circular or slightly elongated basins with simple shorelines and wide entrances that are open to the ocean. -

Category C - Tidal river lagoons
These occur where the mouth of a main river channel connects to shallow lagoons. -

Category B - Tidal river mouths
Elongated basins of simple shape and several to ten metres depth. -

Category A - Coastal lakes
Very shallow basins (several metres depth). They are often elongated and run parallel to the shore. -

What are you eating? NZ scientists reclassify nori – the seaweed used to make sushi
News article06 November 2012 -

Scientists discover freshwater flows affect polar oceanic microbes
News article31 October 2012 -

First sighting of volcano responsible for undersea eruption
News article29 October 2012 -
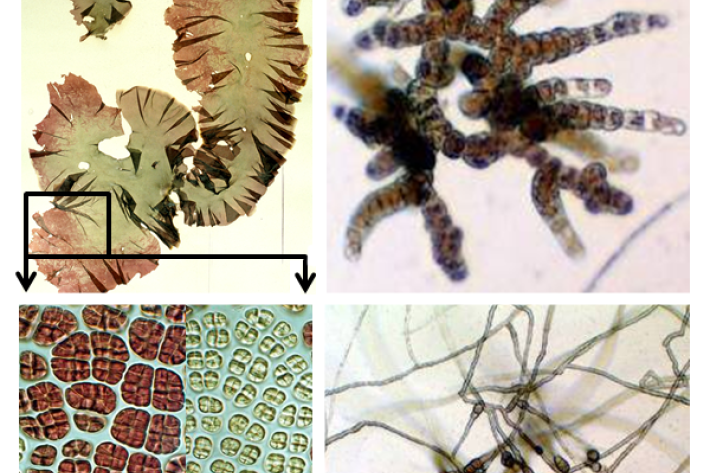
Reclassifying karengo (nori)
Research ProjectThe seaweed known colloquially as nori in Japanese - used for making sushi - or karengo in Maori has been reclassified by an international team of scientists including NIWA's Dr Wendy Nelson. -

NIWA’s Kaharoa sets sail to deploy robots across the Pacific Ocean
News article12 October 2012 -

Kiwi great whites cross the ditch to Bondi
News article26 September 2012

