-
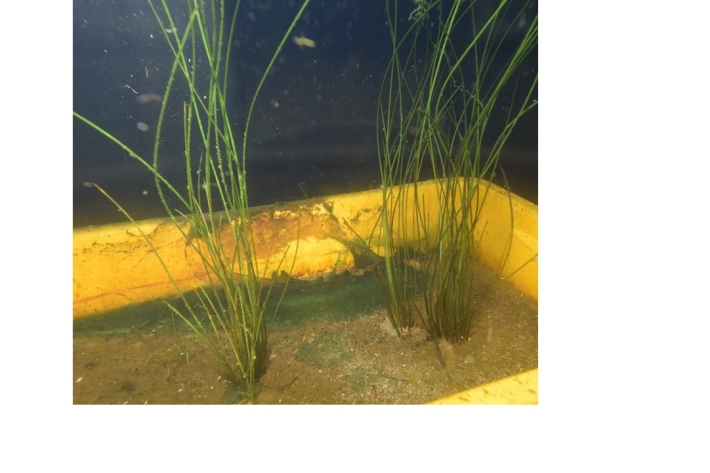

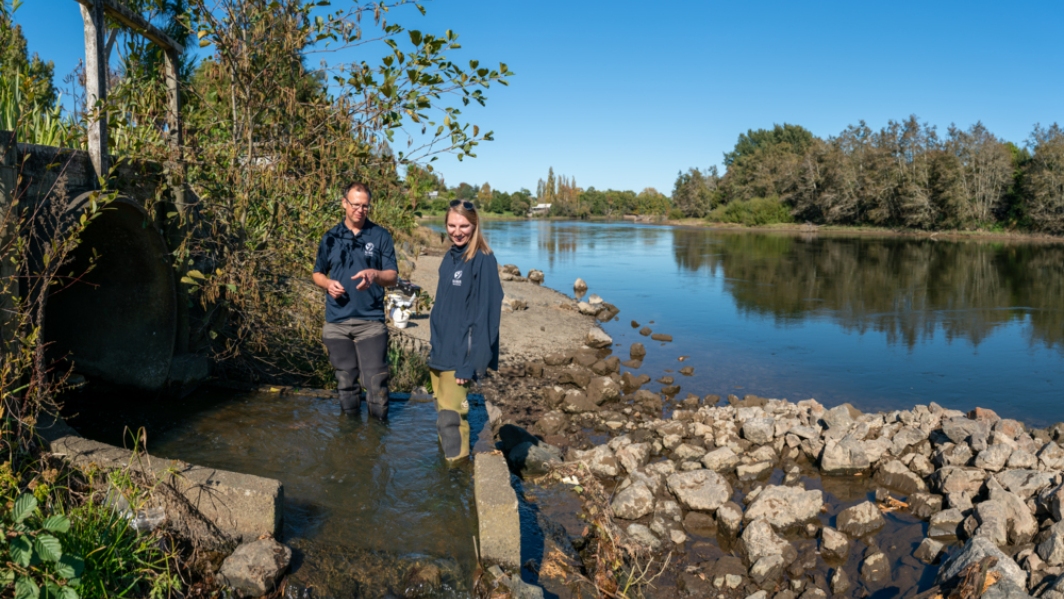
Recovering plants for reintroduction to Lake Ōmāpere
Research ProjectThree plants of an endemic submerged quillwort (Isoëtes) were recovered from Lake Ōmāpere by NIWA in 1998, prior to the lake weed (Egeria densa) dying off and the lake switching into an algal dominated turbid state. No further isoëtes plants have been observed in the lake since that time. -

Waitaki weed surveillance plan
Research ProjectNIWA and Meridian are developing a management strategy on LINZ crown owned lakes for pest aquatic plants – weeds, the alga Didymosphenia geminata (Didymo) and filamentous green algae (both native and introduced) - in the Waitaki Catchment. -

River Environment Classification
Research ProjectThe River Environment Classification (REC) is a database of catchment spatial attributes, summarised for New Zealand's river network. The attributes were compiled for the purposes of river classification, while the river network description has been used to underpin models. -

Modelling channel dynamics in braided rivers
Research ProjectNIWA are contributing to and testing the open source Delft3D model so that it can be used to simulate the response of braided rivers and their ecosystems to the changes in river flow associated with water use schemes, such as dams. -

Mapping our freshwater biodiversity
Research ProjectThe ability to properly manage our freshwater resources requires a solid understanding of the flora and fauna which live in and interact with them. -

Staying ahead of water weed invasions
Research ProjectAquatic systems are under threat due to the introduction of invasive exotic species such as water weeds. Modelling work by NIWA has provided new information on which water bodies may be at greatest risk. -

Fish risk assessment
Research ProjectNIWA has developed a rapid, desktop model which assesses the potential impact of introducing new fish species to New Zealand. -
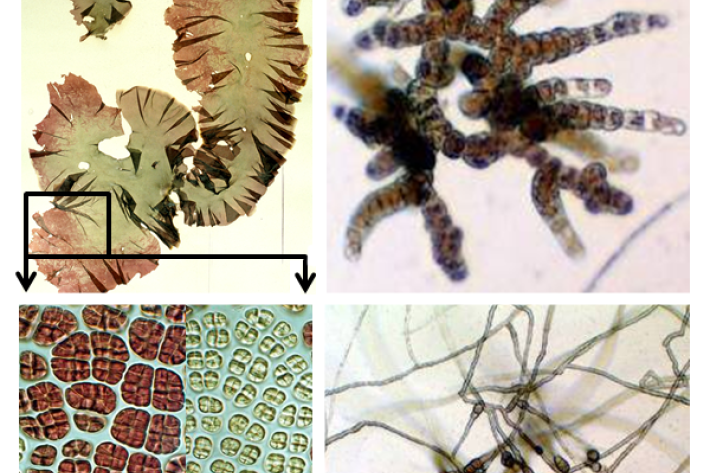
Reclassifying karengo (nori)
Research ProjectThe seaweed known colloquially as nori in Japanese - used for making sushi - or karengo in Maori has been reclassified by an international team of scientists including NIWA's Dr Wendy Nelson. -

Globalisation of aquatic plant pests
Research ProjectNew Zealand's geographic isolation and relatively recent colonization provide the opportunity for a unique genetic analysis of plant movement patterns to be explored. -

Sedimentation in New Zealand estuaries
Research ProjectEstuaries in New Zealand are experiencing sedimentation at higher rates than before humans arrived here: this represents a loss both for land and estuary productivity. We need to better understand what has been happening so that we can predict the future and fight these losses. -

Aquatic weed risk assessment model (AWRAM)
Research ProjectA significant threat to the biosecurity of New Zealand's freshwater habitats comes from plants that have been intentionally introduced. -

Controlling water weeds with grass carp
Research ProjectA Ministry for Primary Industries-funded study has shown that grass carp, in enclosures, can be used as an effective means of controlling invasive plant species in our waterways.

