EFSAP is a water planning and management tool designed to assist with setting regional or large-scale water resource use limits for rivers.
The tool predicts how limits on water take and minimum residual river flows can be designed to optimise reliability of water use and effects on in-stream environments.
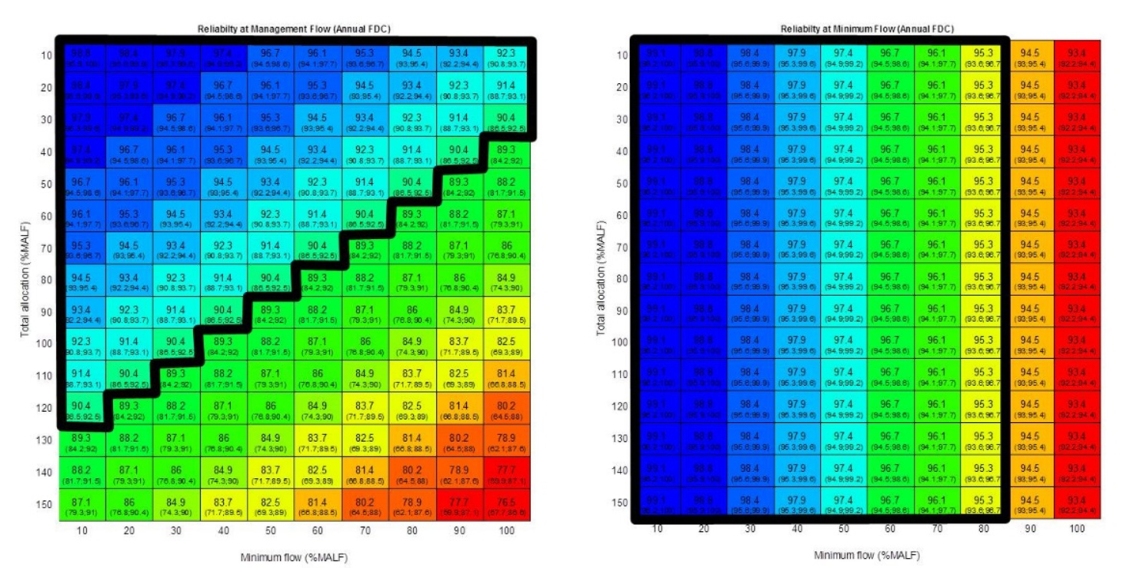
EFSAP simulates how both reliability and security of water supply change when different combinations of minimum flow and total allocation limits are set. Examples of out-of-stream use include domestic water and irrigation. In-stream environmental values include physical habitat for fish.
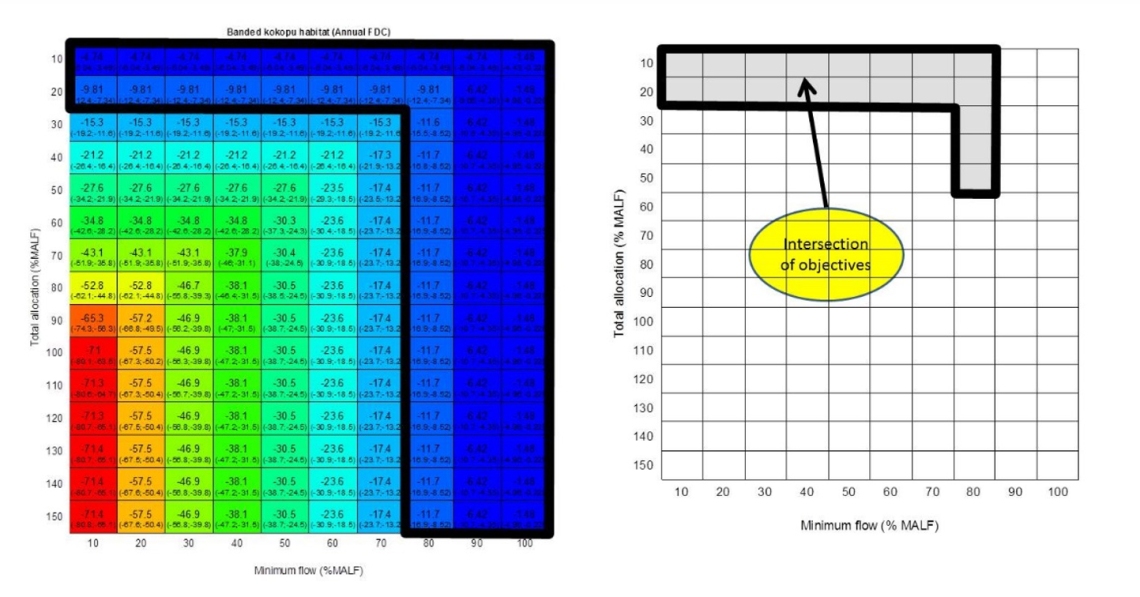
Image caption: Example of evaluating regional objectives for multiple values and determining range of limits that satisfy all objectives. Each box in the coloured decision-space diagrams summarises the consequences of a different combination of minimum flow and allocation limits modelled using EFSAP. Black boxes on the coloured decision-space diagrams represent the limits which meet the objective for each value. The grey shaded box on the bottom right figure is where the other three black boxes overlap and represents the combination of limits that meet the objectives for all three values.
Alternative methods for supplying input information may be applied where data are available from specific local studies or observations. For example, EFSAP allows estimated flow duration to be replaced with measured flow data such as are available for many of New Zealand’s larger rivers and streams. EFSAP also includes the ability to quantify uncertainties in the estimation of reliability and security of supply. Quantifying uncertainties is important in limit setting processes.
Applications
EFSAP has been used by many regional councils, including Northland, Auckland, Wellington, West Coast and Canterbury to help set default or interim water allocation limits in regional plans or inform limit setting processes. Setting regional limits for water-resource use is mandatory under the National Policy Statement for Freshwater Management (NPS-FM).
View report: Simulating consequences of water allocation limits for Auckland [2.5MB PDF]