-
NIWA urges farmers to prepare for climate change
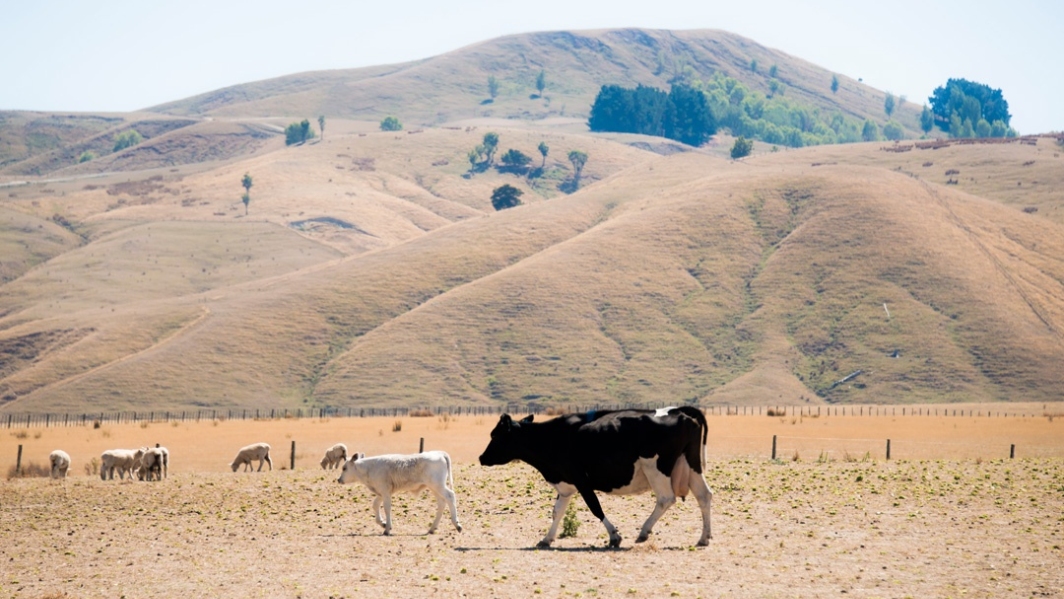
Media release06 June 2018NIWA is encouraging farmers to plan for climate change so they can maximise their abilities to adapt and thrive as significant change begins to take place. -

La Niña's gone; wild and unruly arrives
Media release29 May 2018We've got hot temperatures, we've got cold temperatures, freezing temperatures, ice, snow, hail, rain - and even a few rays of sunshine. And one very confused weather pattern. -

Well-informed, better prepared
Our scientists provide the knowledge key for evidence-based decision-making and for our society as a whole. -
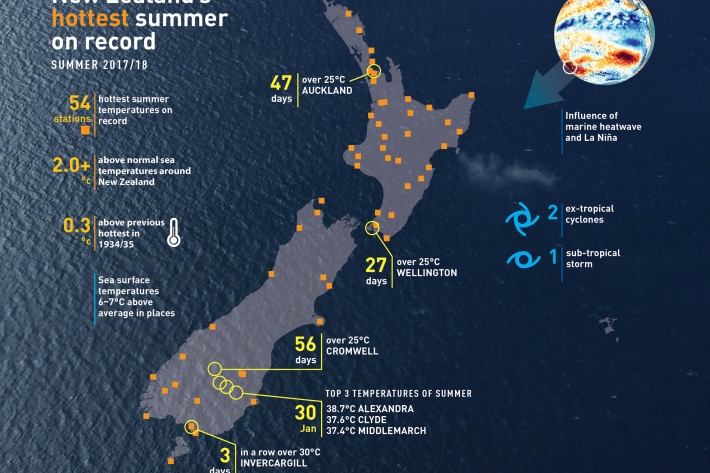
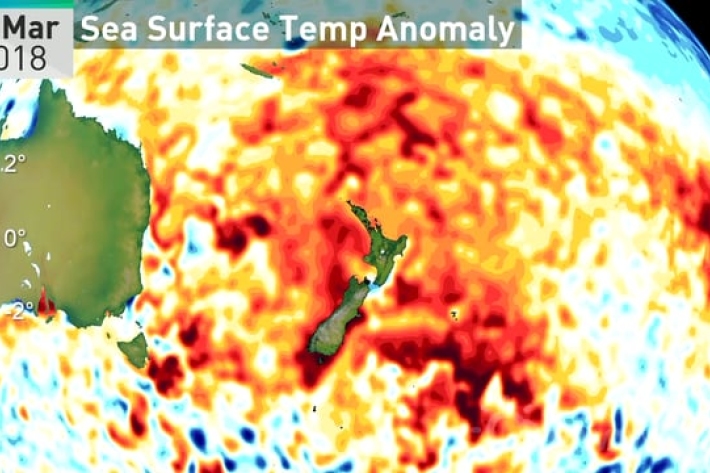
The record summer of 2017/18
Feature story30 April 2018Less than a week before the official end of summer on 28 February, temperatures dropped and a cool breeze made a whistle-stop tour of the country. -
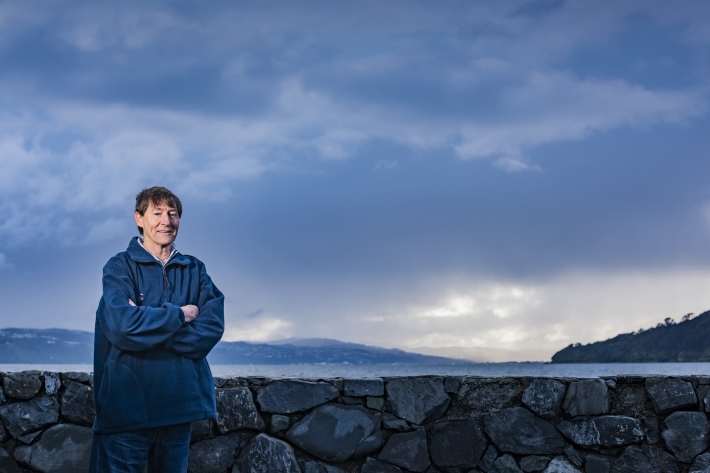

Solutions: Regional climate change
Feature story20 April 2018As climate change takes hold, regional council planning, sustainability and hazard managers are looking to NIWA. -
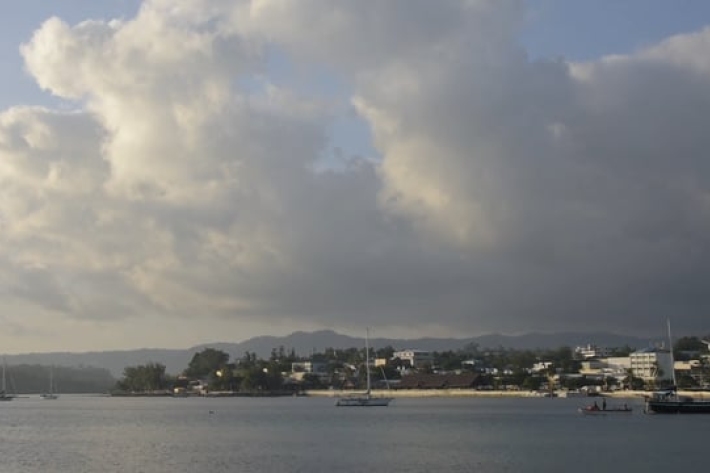

Improved climate information for Vanuatu
NIWA and Vanuatu's Meteorology and Geohazards Department have installed a network of fully automatic weather stations across Vanuatu. -
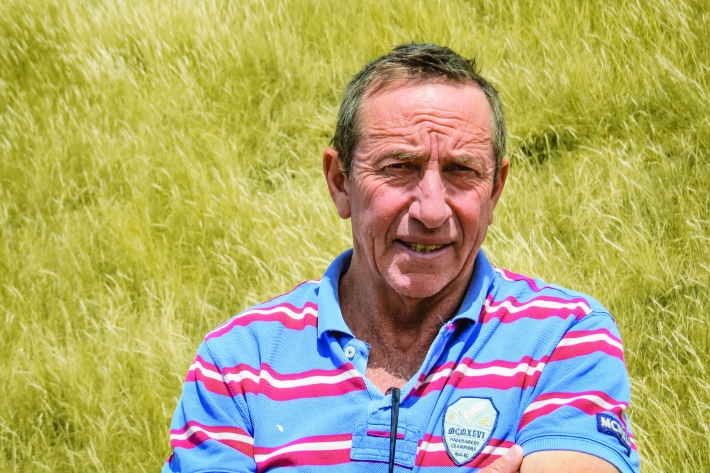

Beating drought
Feature story10 April 2018How a regional climate history helped save a farm and cure depression -
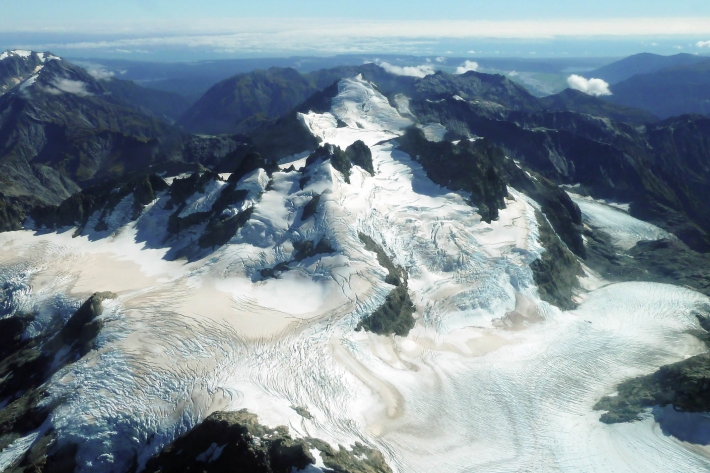

NZ snowline shrinks
Feature story06 April 2018New Zealand’s glaciers have all retreated and lost volume since NIWA started surveying them in 1977. -

New Zealand
New Zealand is situated in the latitudes of prevailing westerlies and exposed coastal locations often experience strong winds, with generally lighter winds elsewhere. -
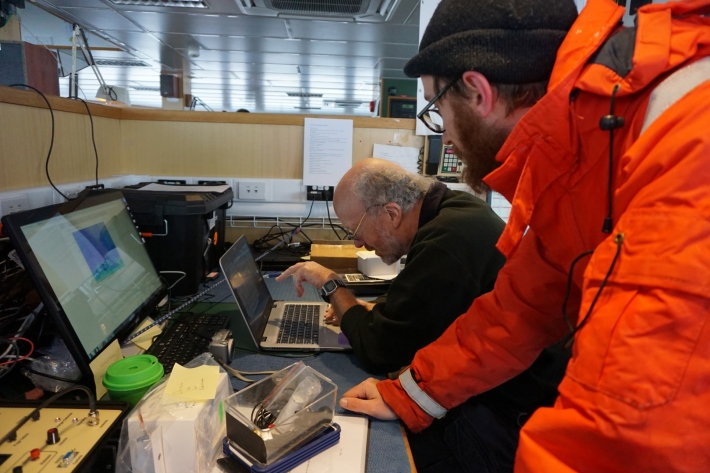

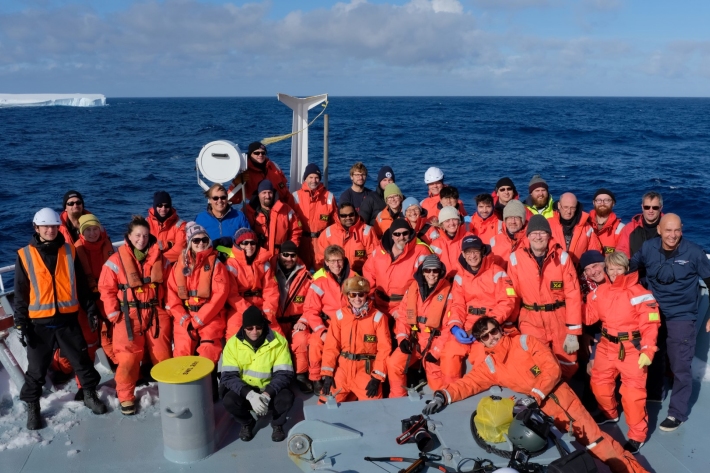
Blog: southern ocean climate models - 13 March
13 March 2018Twice a day at 1pm and 8.30 pm Sean Hartery, NIWA, and Peter Kuma, University of Canterbury, head for the Fantail at the very back of the ship to release their weather balloons.