-

Intensity of cyclones predicted to increase
Feature story05 October 2017Tropical cyclones forming in the south-west Pacific are becoming less frequent but those that do form are likely to be more severe. -
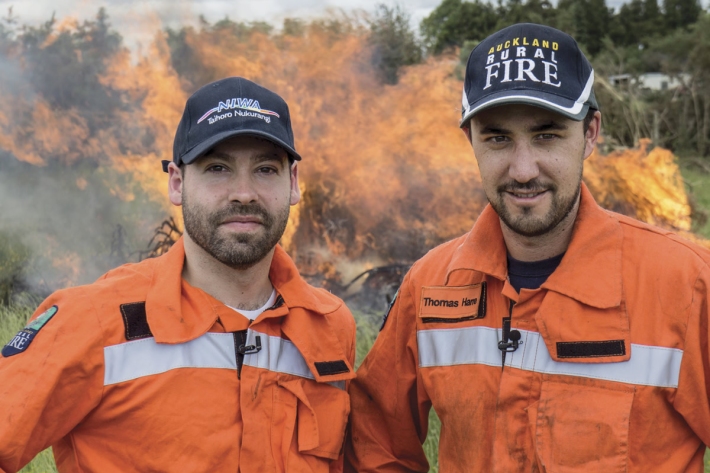

On-call forecasting helps fight fires
Feature story05 October 2017For the past year, NIWA’s meteorologists have been on call to provide real-time, comprehensive information about weather patterns that may accelerate a fire. -

Improved climate information and services in Vanuatu
Feature story05 October 2017The construction of improved climate information and services in Vanuatu has posed unique logistical challenges. -

Production of Hayward kiwifruit in Bay of Plenty at risk from climate change
Media release15 September 2017The most commonly grown variety of kiwifruit around Te Puke will not be commercially viable in the area by the end of the century, say scientists. -
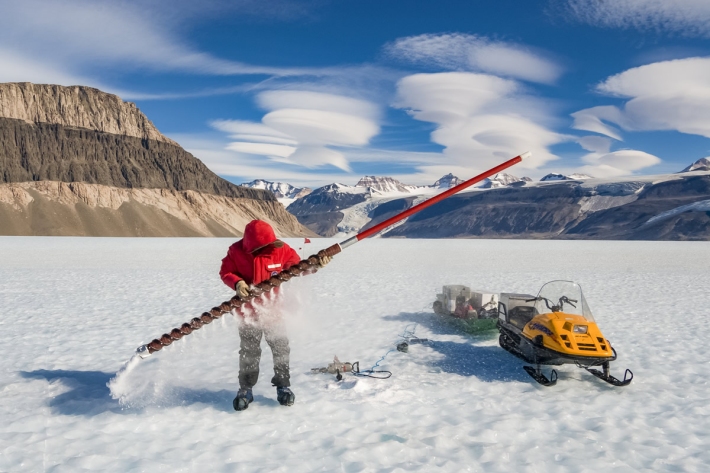

Tiny air bubbles reveal new information about greenhouse gas emissions
Media release24 August 2017Sitting at the surface of Taylor Glacier in Antarctica, are layers of ice more than 10,000 years old. And trapped inside those layers are bubbles of ancient air – like tiny time capsules - able to tell scientists a story about what the world used to be like and how humans have changed it. -
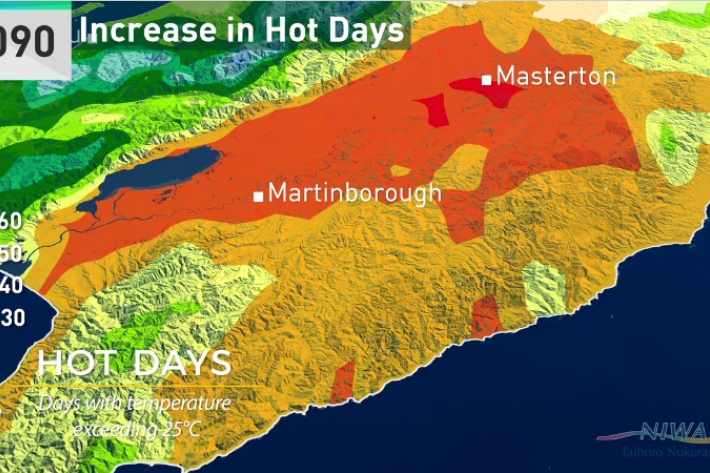
Wellington will get significantly warmer, new climate change report shows
Media release07 August 2017Wellington city will have warmer autumns, almost a month of days over 25°C and up to 10 per cent more winter rain by 2090, according to a new NIWA climate report. -
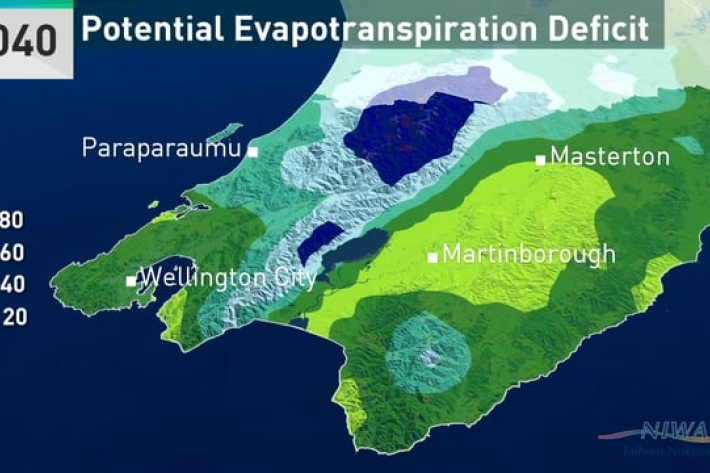
Climate change and variability - report for the Greater Wellington Region
-

Climate change will cause more deaths from air pollution, study finds
Media release01 August 2017New research estimates that if climate change goes unchecked 60,000 more people will die globally from air pollution in 2030 – just 13 years away. -
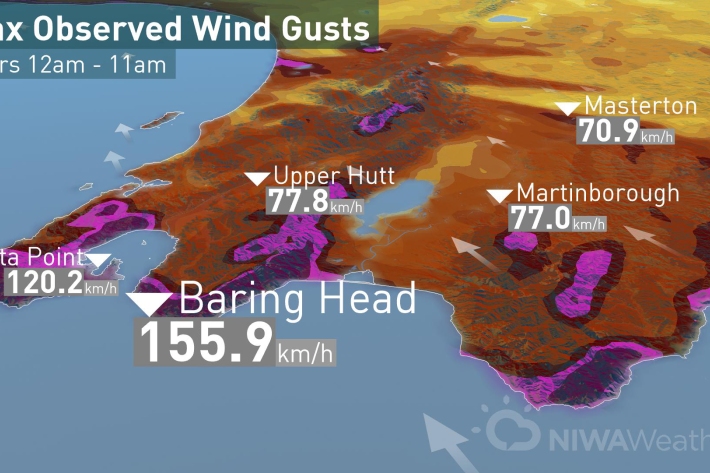
So far, so stormy
Media release13 July 2017Today’s low came spinning off the coast of Hawke’s Bay funneling strong winds through the Cook Strait and hitting Wellington region with strong winds before moving on to Taranaki and Auckland this afternoon. -

Lesson 9: Ngā Tohu o te Taiao – Māori environmental indicators
Education ResourceThis lesson will explore the use of Māori environmental indicators [tohu] to anticipate local weather and climate conditions. -
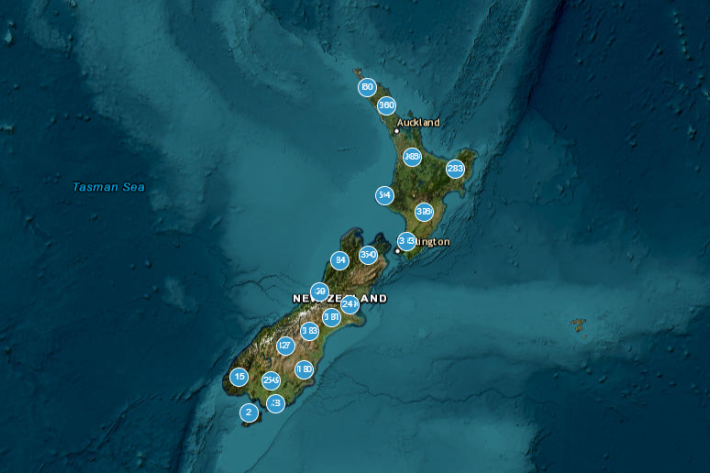
HIRDSv4 Usage
NIWA's High Intensity Rainfall Design System (HIRDS) offers planners and engineers more certainty about the frequency of high-intensity rainfall events, enabling them to better design stormwater drainage, flood defence systems and other vital structures. -
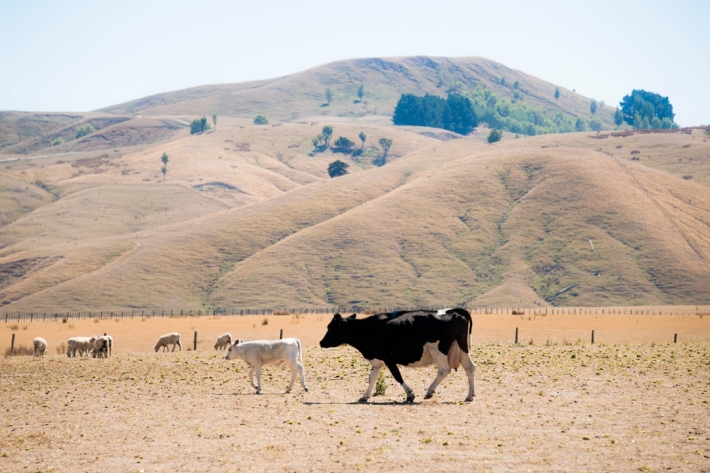

Drought
Education ResourceDefining drought and identifying its causes and impacts on humans.

