-

NIWA ship returns from Antarctica with ‘pieces of a puzzle’
Media release21 March 2018The absence of sea ice near Antarctica over the past six weeks has astonished scientists undertaking research aboard NIWA’s flagship research vessel Tangaroa.
Tangaroa Marine Environment and Ecosystem Voyage 2018 -
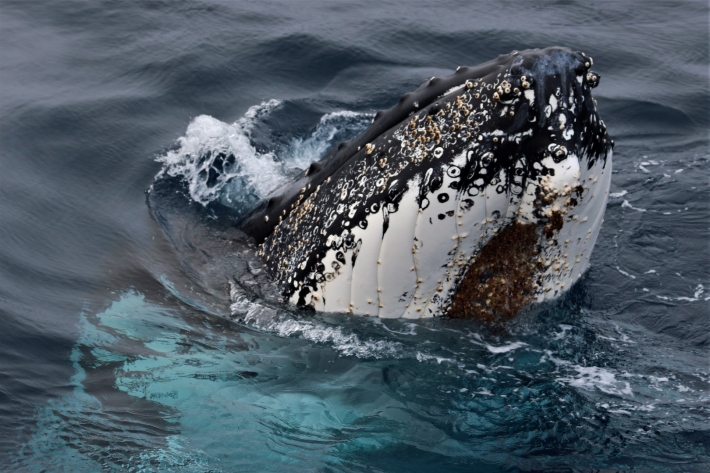

Blog: Passive acoustic mooring - 15 March
15 March 2018A couple of days ago we deployed the last of three long-term passive acoustic monitoring moorings, as a collaboration between the Ross-RAMP MBIE Endeavour project and The Australian Antarctic Division. -
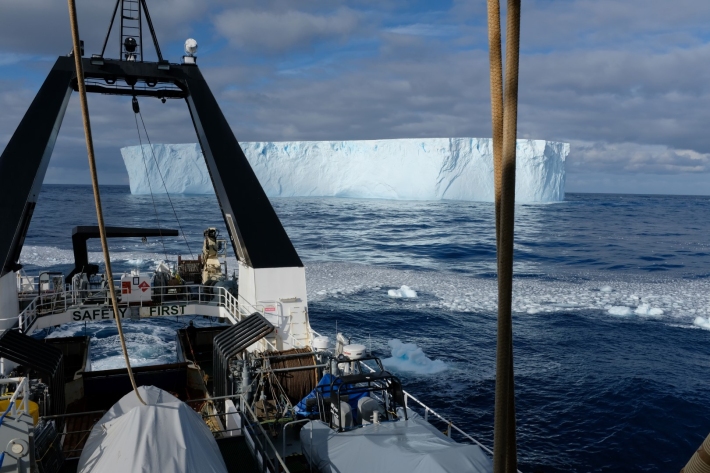

Blog: Time to head home - 17 March
17 March 2018Today we left the area south of 60°S and have started the five-day return journey to New Zealand. -
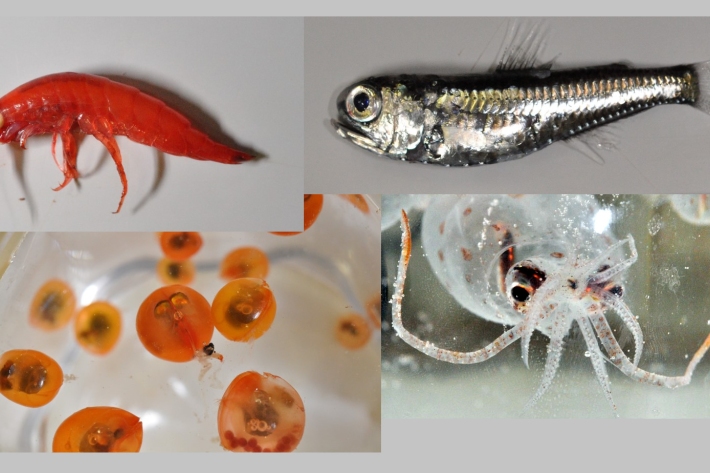

Blog: The inhabitants of the twilight zone of the open-ocean - 15 March
15 March 2018
Think about a futuristic world where at night time, people use different kind of self-propelled vehicles to hover across cities, illuminating the skies with different colours and shapes, while transiting around them. -

Blog: Zooplankton, the pelagic food-web, and carbon cycling - 14 March
14 March 2018 We have been conducting daily net tows to get an integrated picture of the macro-zooplankton dynamics in the area. -
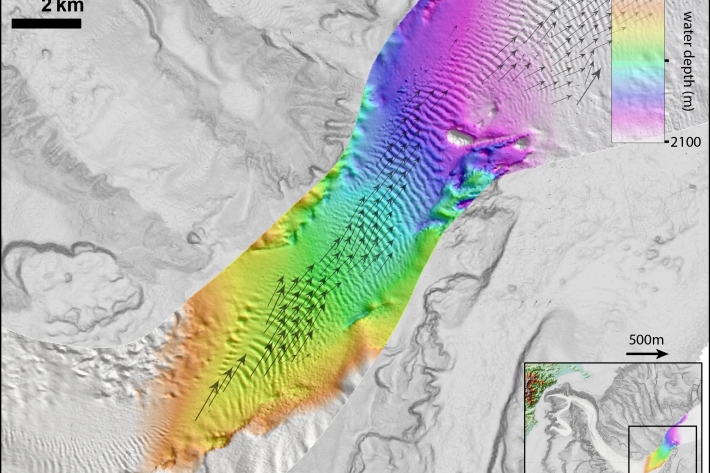
Kaikōura earthquake generated huge submarine sediment shift
Media release15 March 2018The 2016 Kaikōura Earthquake has shown that more than 100 million dumptrucks of mud and sand flow through the Kaikōura Canyon every 140 years, scientists say. -
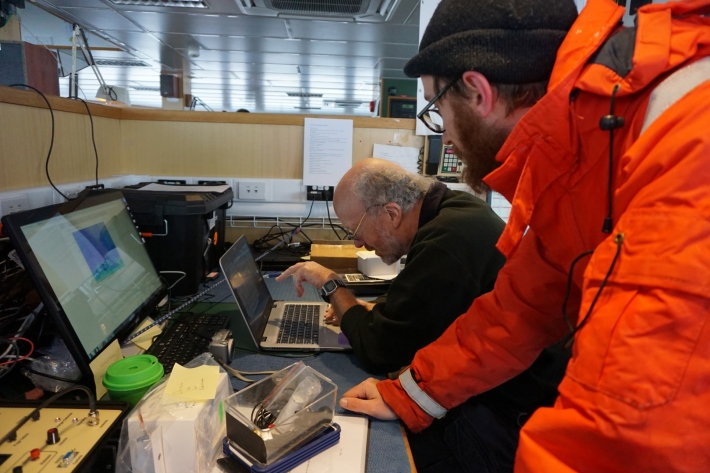

Blog: southern ocean climate models - 13 March
13 March 2018Twice a day at 1pm and 8.30 pm Sean Hartery, NIWA, and Peter Kuma, University of Canterbury, head for the Fantail at the very back of the ship to release their weather balloons. -
Blog: Plankton blooms and clouds - what's the link? - 11 March
11 March 2018 Today we found NIWA’s Andrew Marriner hard at work in the Ocean-Atmosphere Container Lab and asked him to explain his work onboard. -
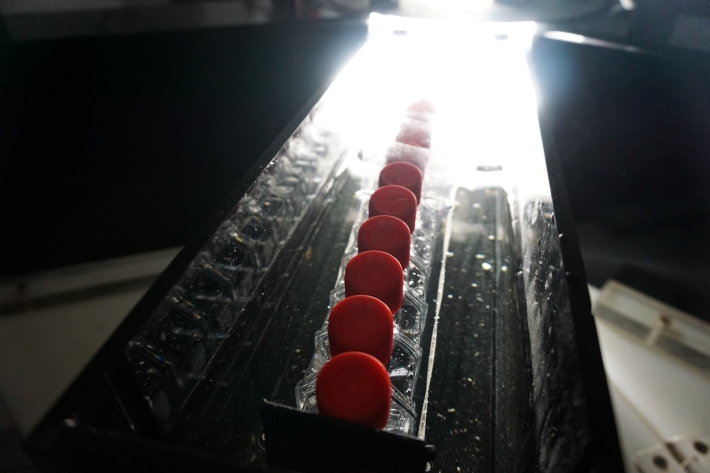
Blog: Radially Aligned Linear Photosynthetron - 9 March
9 March 2018In the back of Karl Safi’s lab, where we found him working in the semi-dark, is a very futuristic looking piece of kit called the Radially Aligned Linear Photosynthetron (RALPH). -
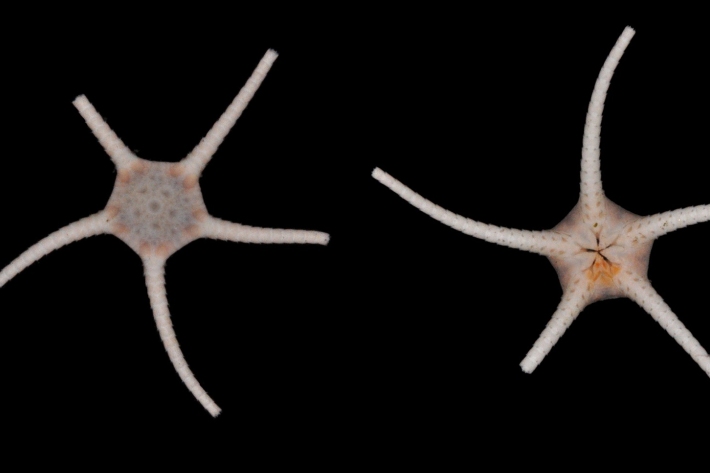

Blog - specimens collected by epibenthic sled - 10 March
10 March 2018To verify the identities of animals we see on the DTIS camera, we use an epibenthic sled to collect physical samples of animals from the seafloor. -
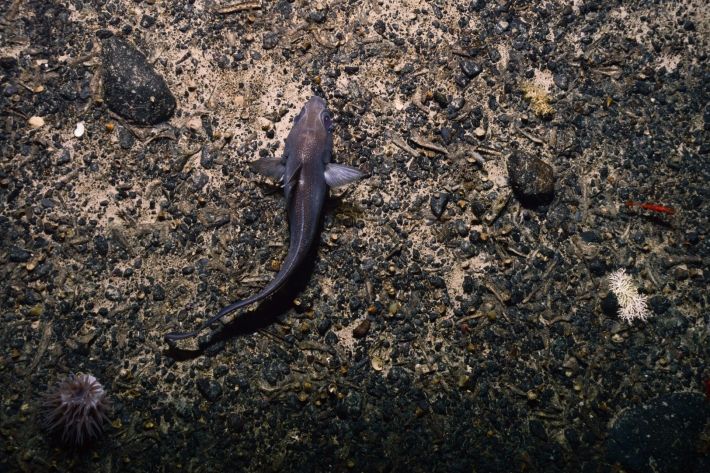

Blog: Long Ridge seamount communities - 7, 8 March
8 March 2018The Benthic team have been observing and identifying animals living on the seabed at Long Ridge, north of the Ross Sea. -

Scientists measure glaciers after record-beating summer
Media release08 March 2018Climate scientists and glaciologists are taking to the skies this week to find out how New Zealand’s glaciers are faring following this summer’s record-breaking warmth.
