The fishery is managed differently depending on the region and specific environmental protection and fishery management objectives in the region.
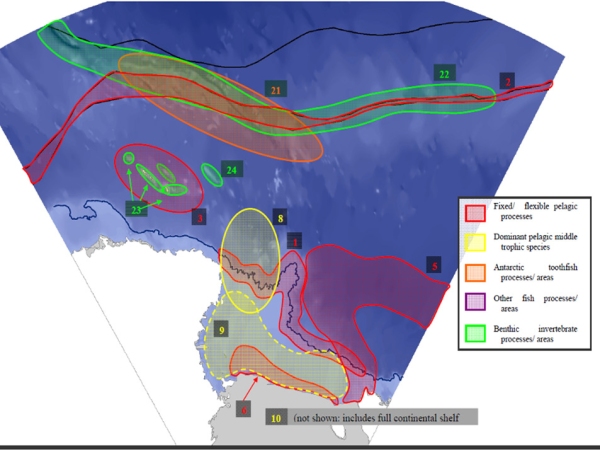
A bioregionalisation process was undertaken to identify where areas of similar characteristics were, and how they could be grouped into bioregions.
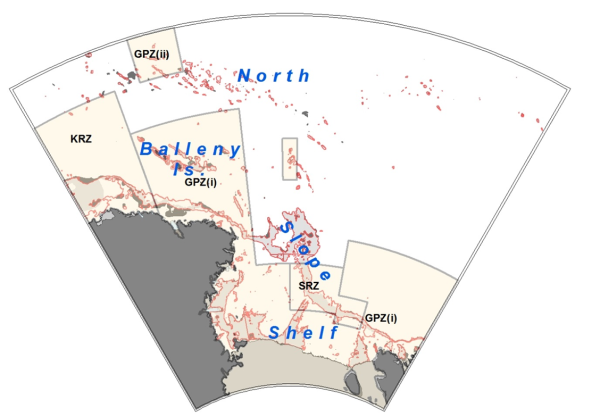
In 2016, a Joint NZ-US proposal for a Ross Sea Marine Protected Area was adopted by CCAMLR to provide protection for key ecosystem components, promote collaborative research in the region, monitor for potential ecosystem effects of fishing, and provide scientific reference areas to disentangle effects due to fishing from effects due to climate change (see Conservation Measure 91-05).
The MPA consists for three zones:
- a general protection zone:
- Balleny Islands, Ross Sea shelf and parts of the Ross Sea slope (i)
- Northern seamounts (ii)
- Scott seamount (iii)
- a special (toothfish) research zone (SRZ)
- a krill research zone (KRZ).
The area covers a total of 1.55 million km2, making it the largest in the world and includes the area under the Ross Ice Shelf.
Under the MPA Conservation Measure, the Ross Sea Shelf is closed to commercial fishing, while areas previously closed to fishing (north and eastern Ross Sea Region) are open for fishing during the normal fishing season.
Separate catch limits are used to control fishing in the North (north of 70° South), Slope, and Special Research Zone.