-
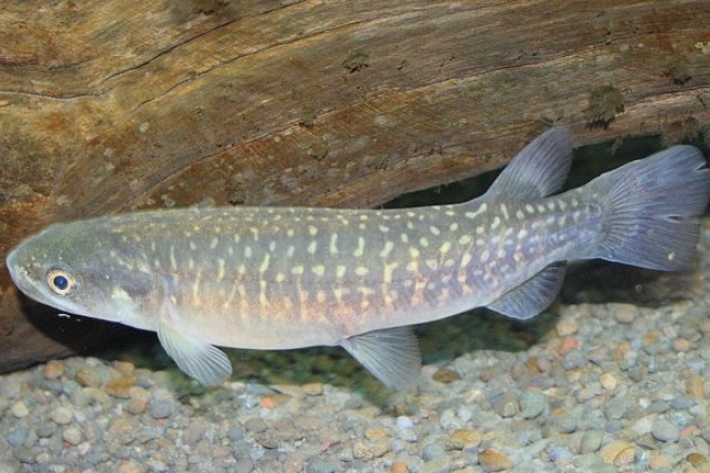

Reintroducing giant kōkopu to Nukumea Stream
Research ProjectThe giant kōkopu is a native whitebait species considered rare and vulnerable. NIWA is working with Mahurangi Technical Institute and environmental consultancy Boffa Miskell to test the feasibility of reintroducing giant kōkopu to Nukumea Stream, north of Auckland. -
Restoration of seagrass beds in Whangarei Harbour
Research ProjectSeagrass beds form an important undersea habitat for small fish, seahorses and shellfish in New Zealand. -

Icebergs
Icebergs approach New Zealand’s sub-Antarctic islands every few years. -
Valuing New Zealand's marine environment
Research ProjectThis unique project is the first systematic attempt to quantify and map environmental values of New Zealand's coastal marine ecosystem. -

Predicting long-term sedimentation and heavy metal accumulation in estuaries
Research ProjectNIWA has developed an Urban Stormwater Contaminant (USC) model to enable urban planners to predict sedimentation and heavy metal accumulation in estuaries and identify problem areas in order to target mitigation measures.