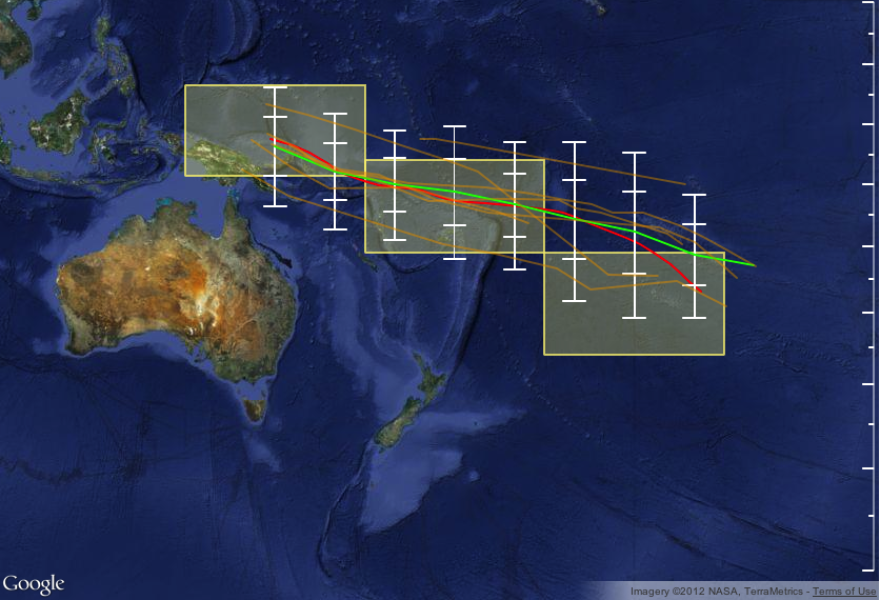
The ensemble of global climate models for rainfall that are used in METPI show an area of higher than normal rainfall associated with the SPCZ position.
The green line indicates the average SPCZ position for the forecast period based on the average of 8 climate models. The white vertical bars and 'whiskers' indicate the one and two standard deviations between the model projections of the SPCZ position every 5 degrees of longitude.
For the coming three months, the dynamical models forecasts indicate that the South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ) is likely to sit very close its to climatological position over most of the southwest Pacific, and be located slightly north of normal in the far eastern Pacific (east of around 160 °W).
The uncertainty in the SPCZ location for the forecast period is highest to the east of the Dateline.